[IT-Security-2] 服務阻斷 Denial of Service Attacks
Denial of Service Attacks
Notes from RWTH Aachen University course
“IT security 2” Wintersemester 2019/20
professor: Meyer, Ulrike Michaela
 What is denial of service attack
What is denial of service attack
- 攻擊availability
- A Denial of service(DoS) is an action that prevents or impairs the authorized use of networks, or applications by exhausting resources such as central processing units, bandwidth, and disk space.
 攻擊的resources分類
攻擊的resources分類
 Network bandwidth
Network bandwidth- 攻擊network links的capacity (如ISP連線)
- intra-ISP能力通常較ISP連到corporate LAN能力高
- 若ISP router收到過多的traffic,會drop packets
 System Resource
System Resource- overloading or crashing OS的Network handling軟體
- Type1: 傳送耗費資源的packets
- SYN spoofing (targets table of TCP connections on a server)
- Type2: packets啟動bug
- reboot機器使reload軟體
- poison packet attack
 Application Resources
Application Resources- 特定applications(如Web server)
- 利用多個合法的requests,使server花費資源回覆requests
- 稱作 cyberslam
- 其他example: trigger server的bug
- Flooding
- overwhelming網路連線能力
- 產生大量traffic (example: ICMP echo requests)
- 容易被偵測如果source address是單一的
- 回傳的訊息仍是大量traffic (reflected back to the source)
 Source Address Spoofing
Source Address Spoofing
- 製造假的IP address (在ICMP flooding時)
- 較難偵測
- 沒有reflection of traffic(回傳訊息的traffic) back to real source
- 給real source IP的reply(可能找不到IP address)加到link to target(回傳給target)
 Thwarting(阻撓) Source Address Spoofing
Thwarting(阻撓) Source Address Spoofing
block 無效的IP packets, 在egress filter
越靠近attacker’s subnet越好
但很多ISP不採用此filter (costly且降低performance)
 SYN spoofing
SYN spoofing- 攻擊network server回應TCP connection request
- overflow the table of 已知TCP connection
- 合法user的request會失敗
 Types of flooding attacks
Types of flooding attacks
- 使網路overloaded
- 使routers擁擠,packet drops
 ICMP Floods
ICMP Floods- 傳統administrators允許ICMP echo request/replies到server診斷
- 現在許多組織用firewall過濾ICMP echo request
- attackers可能轉向其他 ICMP message type
- 必要的通知congestions的訊息
- 帶著部分訊息使他們變得很龐大
 UDP Floods
UDP Floods- UDP packets被導向某個port
- (早期版本) 被導向的packets(假造的source address)可能被預設能通過
- 若有server running service則會回應original packet data內容給假的source address
 TCP SYN Floods
TCP SYN Floods- 用假的source address傳送TCP SYN packets
- flood network link而不是server’s system resource
Application-based bandwidth attack
- 使目標執行resource-consuming的運算
- 攻擊者利用此 Disproportionality(不成比例的) (簡單的query可以使application做大量運算)
- example for two application layer protocols:
- Session initiation protocol(SIP)
- HTTP
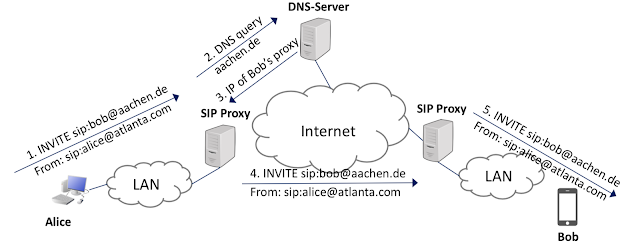
 Session initiation protocol(SIP)
Session initiation protocol(SIP)- 兩種訊息: requests / responses
- SIP INVITE 訊息建立media session
- 攻擊者利用INVITEs訊息進行flood攻擊
 HTTP
HTTP- 用HTTP request轟炸server
- 下載大型檔案(使用memory, processing, transmission資源)
- recursive (recursive link)
也較 spidering
 Slowloris
Slowloris- 通常server有許多threads回應requests
- 攻擊者佔用這些threads,傳送無法完成的HTTP requests
- sends incomplete request
- sends more header lines to keep connection alive
 Principle of Reflection Attacks
Principle of Reflection Attacks
- 攻擊者傳送假的target’s address
- server稱為 Reflector (intermediate)
- server回應此packet並送response給target
- 過度的 responses 會overwhelm target’s network link
- 容易deploy且難偵測
- Ideal: 一個request有大量response(eg. DNS, SNMP, ISAKMP等)
- server通常有high-capacity with good connection
- eg. SYN flooding attack using reflection
 Self-contained Loop
Self-contained Loop- 攻擊者用 echo reflector service 和 port 7
- target若在port 7收到response,則視為echo request,並echos back
- 如果它們沒有filter不可能的port組合,則產生self-contained loop
 Amplification Attacks
Amplification Attacks
- 產生多個response給target
- 送廣播的request
- 所有的host都會回覆這個request,產生大量response
 Defense against this broadcast amplification
Defense against this broadcast amplification
- 不允許從network外的broadcast
- 但目前沒有被廣泛採用
 DNS Amplification Attacks
DNS Amplification Attacks
- target: DNS server
(reflector也是 DNS server) - 利用DNS protocol會轉換small request成 large response
- 越新的DNS版本效果越好
因為允許responses超過4000bytes (需要DNSsec的public key)
 Defenses against DoS attacks
Defenses against DoS attacks
- 減少變成target的後果
- 避免系統成為被利用的對象
- 很難避免
- 有些traffic可能是意外
- 規定network bandwidth
- 分散server
 Attack prevention and preemption(搶佔)
Attack prevention and preemption(搶佔)- backup resources
- 加強policy
- 修改system或protocol
 Attack detection and filtering
Attack detection and filtering- 偵測攻擊
- 使被攻擊的影響最小
- 偵測可疑patterns
- 過濾packets
 Attack source traceback and identification
Attack source traceback and identification- 識別source
- 通常不可能快(攻擊已送出)
 Attack reaction
Attack reaction- 減輕影響
 Preventive mechanisms
Preventive mechanisms
- 限制傳送假的source address的packet
- 過濾packet types(eg. ICMP, UDP)
- 對付SYN spoofing攻擊: 用修改的TCP版本
- server不用存取connection資訊直到client回傳
ACK - TCP connection table就不會被假的IP佔據
- 缺點:
- server需計算cookie
- 不能用TCP的特定extension (cookie太小)
- server不用存取connection資訊直到client回傳
- 對付SYN spoofing: 選擇性或隨機drop TCP connection table 的 incomplete connections
- 修改table size, 修改timeout
- 對付amplification攻擊:
- 封鎖 IP-based broadcast的使用
- 封鎖可疑的服務或port組合
- 確定另一方是否為人類 (用CAPTACHAs)
 Responding to a DoS Attack
Responding to a DoS Attack
- 組織: ISP在沒有網路連線時available
- traffic可以被過濾
- 發布intrusion detection system以偵測異常traffic
- 擷取packets以分析攻擊type
- 若系統中的bug被攻擊則修改
- 被攻擊後用backup server
Readings
Stallings and Brown “Computer Security”
§Chapter 7 on Denial of Service attacks




留言
張貼留言