[Quantum Information] Evolution
Evolution
Notes from RWTH Aachen University course
“Quantum Information” Summer semester 2020
professor: Wegewijs, Maarten
Evolution
probability should stay probability \(\Rightarrow\mathcal{E}\) is a stochastic map.
Positivity Preservation (PP): \(\mathcal{E}(\rho)\geq 0\)
Trace Preservation (TP): \(\text{tr }\mathcal{E}(\rho)=1\)
🧐 These are general restrictions for quantum evolutions?
- ❌ Difficult in principle: because of entanglement
- ❌ Difficult in practice: PP is more complicated than complete positivity
⭐️⭐️⭐️ Evolutions (superoperators) correspond to states (operators)
\(\rho'=\)\(\sum_m M_m\)\(\rho\)\(M_m^\dagger\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) \(\sum_m|M_m\rangle\langle M_m|\)
We take maximally entangled pure state \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}|\mathbb{1}_{AB}\rangle=\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\sum_i|i_A\rangle\otimes|i_B\rangle\]
\(\sigma_{AB}\)\(=(\)\(\mathcal{E}_A\)\(\otimes\mathcal{I}_B)\)\(\frac{1}{d}|\mathbb{1}_{AB}\rangle\langle\mathbb{1}_{AB}|\)
\[\sigma_{AB}\xleftarrow{one-}\xrightarrow{to-one}\mathcal{E}_A\]
example:
\(\mathcal{E}_A\)\(=\lambda_0\mathbb{1}_A\bullet\mathbb{1}_A+\lambda_1 Z_A\bullet Z_A\)
\(\sigma_{AB}\)\(=\)\(\frac{1}{2}\)\(\lambda_0|\mathbb{1}_{AB}\rangle\langle \mathbb{1}_{AB}|+\lambda_1 |Z_{AB}\rangle\langle Z_{AB}|\)
- Finite-time evolution
\[ U(t) = e^{-iHt} \\ H: \text{Hamiltonian},\ H^\dagger = H \\ H \text{ and } H+\varphi \text{ describes the same evolution for any } \varphi \in \mathbb{R} \]
Evolution in presence of entanglement: Quantum Channels
- Linear map
- Hermicity-preserving map (HP): \(\rho_A=\rho_A^\dagger\Rightarrow\mathcal{E}_A(\rho_A)=(\mathcal{E}_A(\rho_A))^\dagger\)
- Completely-positive map(CP): \(\rho_{AB}\geq 0\Rightarrow \mathcal{E}_A\otimes\mathcal{I}_B(\rho_{AB})\geq 0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) PP \(\Rightarrow\) HP
- Trace-preserving map(TP): \(\text{tr }\mathcal{E}(\rho)=\text{tr }\rho=1\)
- Complete positivity preservation: How is the input state prepared?
- Any mixed input state on A ultimately arises from entanglement with some preparation system B:
- A superoperator \(\mathcal{E}_A\) is called completely positive (CP) when it preserves positivity even when extended to act "trivially" on any preparation ancilla B in any joint state
\[\rho_{AB}\geq 0 \Rightarrow \mathcal{E}_A\mathcal{I}_B(\rho_{AB})\geq 0\]
\[PP\neq CP\]
- PP-non-CP: negative probabilities
- example: transposition superoperator \(\mathcal{E}_A(\rho_A)=\rho_A^{T_A}\)
⭐️⭐️⭐️ The difference between PP and CP constitudes what is quantum about evolution: Entanglement
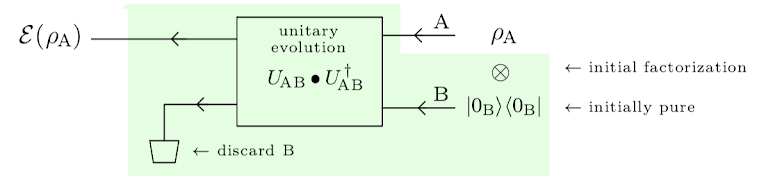
Measurement model for evolution
- 🧐 What state-evolutions can we get by coupling to an inaccessible system (B) in a pure state?
- \[\rho_A'=\mathcal{E}_A(\rho_A)=\text{tr}_B\{{U_{AB}(\rho_A\otimes |0_B\rangle\langle 0_B|)U_{AB}^\dagger}\}\]
- 🧐 What state-evolutions can we get by coupling to an extra system (B) in a pure state, measuring it, and discarding the complete outcomes?
- Projective measurement \(\{\mathbb{1}_A\otimes|b_B\rangle\langle b_B|\}\) in B-basis \(|b_B\rangle\)
- Discarding complete outcome b
- \[\mathcal{E}_A(\rho_A)=\sum_b p_b\rho_{Ab}=\sum_bM_{Ab}\rho_AM_{Ab}^\dagger\]
🧐 Are evolutions derived from measurement models indeed CP-TP maps?
- ⭕️
🧐 Does every operator-sum evolution \(\mathcal{E}_A\) correspond to a unique model \(\{U_{AB},|0_B\rangle\}\)?
- ❌
- Nonuniqueness comes from
- \(\langle b_B|\) \(U_{AB}|c_B\rangle\)
- \(M_{Ab}=\sum_{b'}\)\(\langle b_B|b_B'\rangle\)\(M_{Ab}'\)
🧐 Given any CP-TP map \(\mathcal{E}\) how to compute a set of measurement operators \(\{M_k\}\)?
- compute a bipartite state corresponding to \(\mathcal{E}\) \[\sigma_{AB}=(\mathcal{E}_A\otimes\mathcal{I}_B)\frac{1}{d}|\mathbb{1}_{AB}\rangle\langle\mathbb{1}_{AB}|\]
- Diagonalize it \[\frac{1}{d}\sum_k|(M_k)_{AB}\rangle\langle (M_k)_{AB}|\]
- write down operator sum with operators \(M_k\) \[\mathcal{E}=\sum_kM_k\bullet M_k^\dagger\]
These are called canonical measurement operator.
Purification of evolution = tomography+purification
\[\frac{1}{d}\mathbb{1}_A=\text{tr}_C\frac{1}{d}|\mathbb{1}_{AC}\rangle\langle\mathbb{1}_{AC}|\]
Readings






留言
張貼留言